| You are working on building a residential township for Trump Towers in Romania. One of the vendors who was to provide the bricks mentioned that he cannot provide the same next week, opposite to what he promised. However, you cannot raise finger on him since the time-frame is not mentioned anywhere on your contract with the vendor. You confirmed from the steel-bars vendor that he will provide the steel rods at $50 per piece however, he mentioned that since the price of steal increased since the agreement was signed, hence he can no longer afford it on the price and you need to pay $60 per piece. You are not sure about the weather conditions so you need to procure a software from weather application vendor that will help you to know in advance when it will rain. |
Procurement: The procurement refers to the formal way to obtain any service or a product.
Here is a snippet of various processes that are distributed across multiple phases of a project:
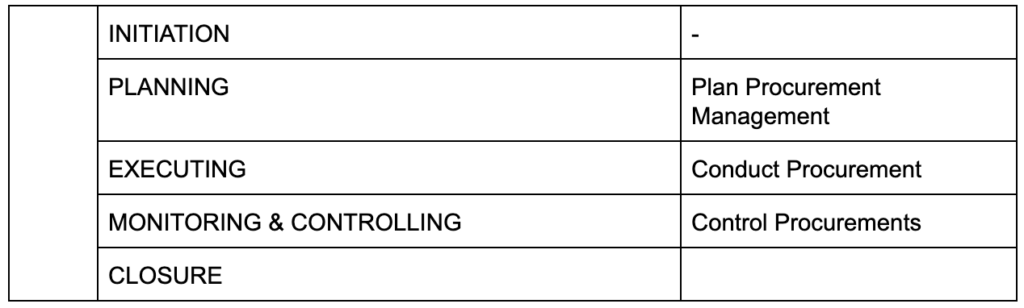
Phase: PLANNING Knowledge Area: PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT
The procurement management plan helps to strategise the procurement method, the type of contracts are made with vendors. This is not about the role of attorney or lawyers but of the project manager in the procurement.
SELLER : The person/organization who provides goods or services is known as the Seller.
BUYER : The person or organization that is purchasing the service/goods is called Buyer.
Role of a PM in the contract is usually blurred when there is already a procurement manager involved in the process. So as a Project Manager following are the roles and responsibilities:
Plan Procurement Process includes following important steps:
Types of contract depends on various factors like:
[IMP] Based on the above factors there are 3 types of contracts:
FIXED PRICE
The fixed price contract is the one that has the well defined specifications. In case the costs are more than assumed then the seller needs to bear the cost. Hence, the buyer has lesser risk.
TIME & MATERIAL
The Time and Material has the buyer to pay based on the per-hour or per-item basis based on the consumption . This contract has simpler terms of negotiations. Since the seller’s profit is based on the time you spend more and hence no benefits on completing the project earlier.
COST REIMBURSABLE
When the exact project specifications are not known and hence the costs cannot be determined. This enables the seller to pay the allowable incurred costs.
There are multiple types of Cost Reimbursable contracts:
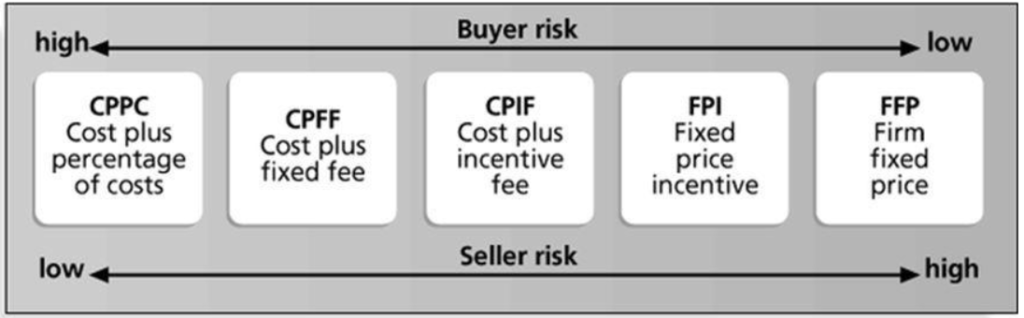
Cost Plus Percentage of Cost (CPPC): The seller pays the cost of the work and a percentage of that work’s budget as the fee for buyer like project cost and 5% of the cost
BID DOCUMENTS: Once the contract is selected, there is a need for buyer to create a bidding document which describes the buyer needs, following are the relevant documents:
Non Disclosure Document: At times the seller do not want the public or their competition to know that they are procuring the item/service. Hence they ask buyers to sign a Non Disclosure.
Phase: EXECUTION Knowledge Area: PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT
The process of conducting the procurements includes getting the bid documents, analysing and selecting the best bid based on defined criteria. There are multiple ways by which the procurement requests can be sent out like:
Seller Proposal: The seller’s response to the proposal to the bid documents is called seller proposal.
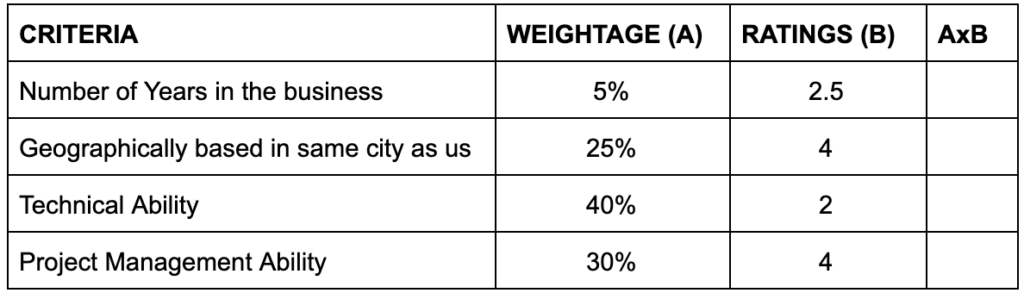
Weighting System: There could be certain parameters to select the best bid, however not all parameters are equal. Some may contain more weightage than the others. A sample of the weightage is shown below:
Items to negotiate: There are multiple factors that can cause the negotiation between buyer and seller, the important factors could be:
Several other factors could be risk, quality, authority, payment schedule etc.
Phase: M&C Knowledge Area: PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT
The process of managing the entire legal relation with respect to the contract terms is taken care in the control procurement process. This ensures that the contract is closed as per the predetermined clauses.
Close Procurements: The formal process of the closure of the contracts once the work is delivered, verified and payments completed.