| Management has decided to assign you as the Project Manager to create a mobile app for visitor management. The app is to be built on the Android and IOS however you are not getting the team with adequate skills, also they are given to you for lesser time period than you want. You are facing trouble to understand who is doing what and when. The team mates often told you about tasks that take days to be completed which others could do in few hours. |
Resource Management: The process to ensure that the project team works on all the work required and ONLY the work required; in order to complete the project successfully.
| The features and functionalities that define a product are known as product scope. Example: For the ZARA app, the product scope is the login with facebook, registration feature, wishlist, cart etc | The complete activities and work done to deliver a product or service, along with the features and functionalities. Project scope includes Product Scope as well in it and other additional activities. Example: In addition to all the features mentioned in product; it also includes license and agreement for 3rd party to get payment gateways, identifying the risks involved to build the app, manage the team to work etc |
Here is a snippet of various processes that are distributed across multiple phases of a project:
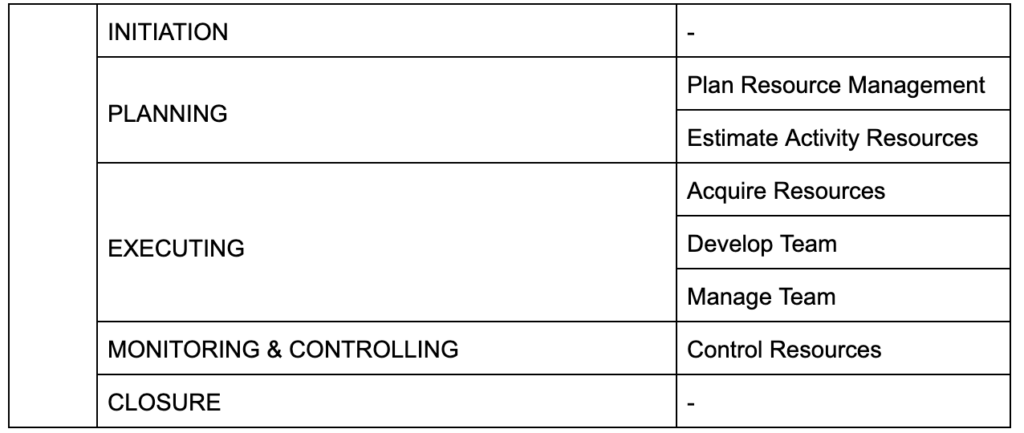
Phase: PLANNING Knowledge Area: RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
This plan is an umbrella for all the resources to be used whether the human resource or other physical resources needed for the project. This also deals with the concepts like how will resources be managed, their cost, how to acquire etc.
Before we discuss further, there are a few important terms that PM should always keep in mind:
Lean: The lean suggests to remove waste from the process. Agile is a derivative of this approach. It recommends efficient use of the resources.
Kaizen: Kaizen is a japanese approach that means “continuous improvement”. This is an important term in Quality Management.
Just In Time: The JIT approach refers to get the resources just before they are needed and avoid any sort of hoarding including inventories, raw materials, supplies etc.
Resource Management Plan: The resource management plan is elaborated plan that is the major outcome of this process. It deals with the human resources and physical resources.
HUMAN RESOURCES
PHYSICAL RESOURCES
Team Charter: This is a project specific document that team creates to establish the approach they will be following like communication, decision making etc
Phase: EXECUTION Knowledge Area: RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
In this process the needs of the resources for the project is determined. The PM recognizes what type of and what number if resources are required.
Based on the inputs above the PM designs the resource histogram chart that helps to visualize the usage of the resources for the work.
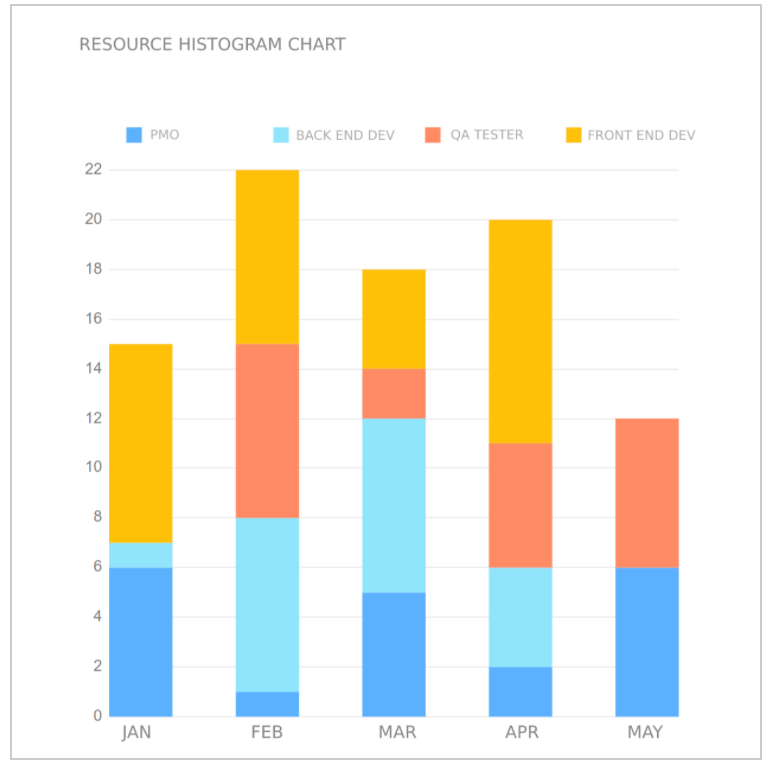
The PM uses scope baseline, schedule baseline etc to determine the relevant resources needed to complete the work in defined boundaries.
Phase: EXECUTION Knowledge Area: RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
In order to execute the project, the PM needs to secure all the human and physical resources as necessary. This process helps to acquire the resources as per the Resource Management Plan.
There are few factors needed for the acquiring of the resources:
There are following types of Resources:
Virtual: When the teams are not in same geography
Phase: EXECUTION Knowledge Area: RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Once you capture all the required resources, now is the need to build the team. This is an on-going process that goes on. The building of teams is where the leadership and other management skills comes into the picture.
Following are some important motivation theories for team building:
[IMP] McGregor’s Theory of X and Y:
As per McGregor, there are 2 catagories for the workers.
Category X: The managers who believe the workers needs to be checked every minute (micro-managed). Their perception is that their are incapable.
Category Y: They believe that employees are much more willing to work with freedom and hence they can route their efforts when given liberty.
[IMP] Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs:
As per Maslow, the needs of the employees vary from low to high as shown in the pyramid.

McClelland’s Theory of Needs: This theory suggests that people can be motivated by one of the following 3 needs:

[IMP] Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory of Motivation: Herzberg’s theory states the same factors does not satisfy and motivate the employees, but these are 2 segments:
HYGIENE: This is a necessity for workers, if not done right would destroy motivation. However, if done right, then also it may not boost the motivation.
MOTIVATING AGENTS: The team is motivated by the work itself.
[IMP] The team building is considered more of a technique based activity. Following are the major stages of team building (in following chronology):
Recognition and Rewards: The team’s performance is one of the outcomes of this process which act as the data points for the PM to understand the need of continuous improvements.
Phase: EXECUTION Knowledge Area: RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
This is an ongoing process to handle and manage the team. This involves daily operational tasks.
There are multiple ways of leading and managing the team, primary styles of leading are mentioned below:
There are some other styles that are good for conflict resolving:
[IMP] Laissez-Faire: The French name translates to “allow to act” which implies that the manager is not directly involved with the team.
POWERS OF PROJECT MANAGER
[IMP] SOURCES OF CONFLICT
CONFLICT RESOLUTION TECHNIQUES
Emotional Intelligence:The ability to recognize and express one’s emotions appropriately and to perceive & manage the emotions of others using observation, communications and interpersonal skills.
Phase: M&C Knowledge Area: RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
This process unlike the above two, focuses on the physical resources. It focuses on the cost, amount and quality being used compared to what was planned.
The resource plan indicates how resources should be utilised, controlled and eventually released.
PMIS: The Project Management Information System (PMIS) is used to analyse, track and access the data on the usage of the resources.